Program Learning Outcomes
Program-Level Learning Outcomes
The program-level learning outcomes align with the CanMEDS 2015 framework as well as with the College of Family Physicians of Canada CanMEDS Family Medicine framework and the Indigenous Health Supplement Key and Enabling First Nations, Inuit and Metis Health’s core Ccompetencies.
The learning outcomes of our program are grouped thematically under the following eight roles, with the expectation that a competent graduating future physician seamlessly integrates the competencies of each:
- Health Advocate
- Collaborator
- Professional
- Leader
- Scholar
- Communicator
- Medical Expert (the integrating role)
- Self
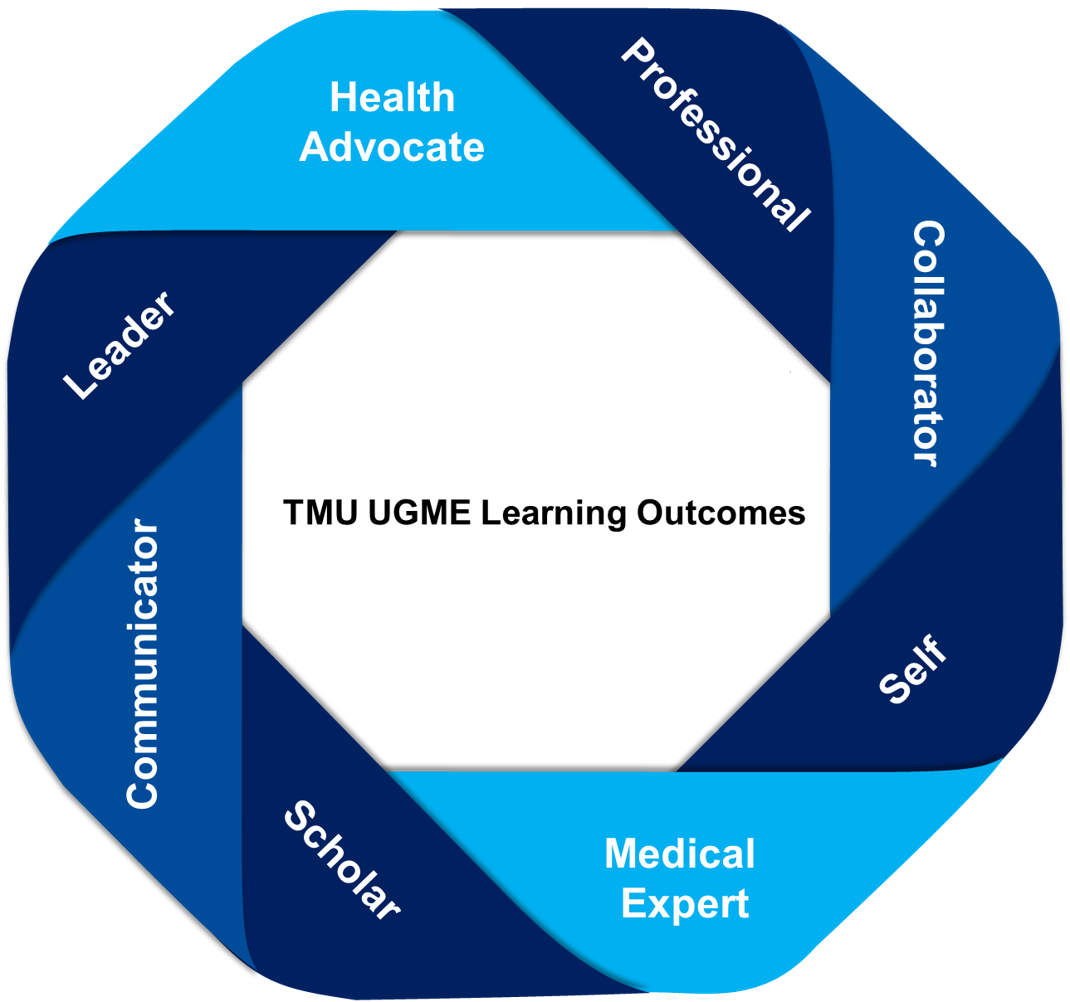
Figure 1: A visual representation of the TMU School of Medicine's program-level learning outcomes.
The CanMEDS framework features seven roles. We have augmented this framework to reflect our program’s distinct philosophy. Medical curricula are usually driven by the Medical Expert role. Indeed, this role is placed at the centre in the pictorial that CanMEDS has created to depict the roles. However, the intended student-focused philosophy of our program’s curriculum, and the goals of the Ontario Quadruple Aim, led to the creation of an additional student outcome role.
The new role we have adopted for our MD program is titled “Self”. It is intended to convey the importance of bringing one’s authentic self, as a human being, to every facet of one’s life, including the professional aspect, while acknowledging the critical nature of supporting the development of personal wellness and success. Therefore, the articulation of learning outcomes in our proposed curriculum, which begins with the Health Advocate and Leader roles, culminates with both the Medical Expert and Self roles. The relationship of the eight roles in our curriculum is depicted in Figure 1.
Program Learning Outcomes: Snapshot
These 'snapshot' outcomes provide a quick summary of the UGME learning outcomes and are a condensed version of the detailed Program Outcomes. The full set of UGME learning outcomes is still central to the program’s curriculum; they also help in course planning and learner assessment.
Synthesize and apply knowledge of the factors influencing healthcare in order to engage in person-centred care that promotes health, health care access and equity for all while respecting persons’ rights to self-determination/self-advocacy.
Build and maintain mutually beneficial relationships with patients, colleagues and the broader healthcare team in order to deliver and improve upon equitable, high-quality person-centred care.
Uphold human rights and adhere to professional and ethical codes, laws and standards of practice in the delivery of equitable and inclusive health care.
Engage as a leader in service to the community to manage change, innovate and plan for the continuous improvement of person-centred care.
Integrate theoretical and empirical knowledge and methods from the biological, clinical and social sciences along with contextual factors in addressing complex health care issues for the benefit of individuals and society.
Adapt verbal, written and electronic communication strategies to the needs of patients, colleagues, teams and institutions to convey well-organized and accurate information in the delivery of health care.
Clinical Assessment
Perform comprehensive and culturally respectful clinical assessments to arrive at viable differential diagnoses and propose investigative and management steps
Planning and Giving Care
Evaluate patient assessment and investigation results as well as patient context to initiate management plans in a variety of circumstances (chronic, urgent or emergent), and plan for continuity of care when indicated.
Identify and build upon individual and system-level strategies and resources to promote your own personal and professional well being.