Facilities

The facility features:
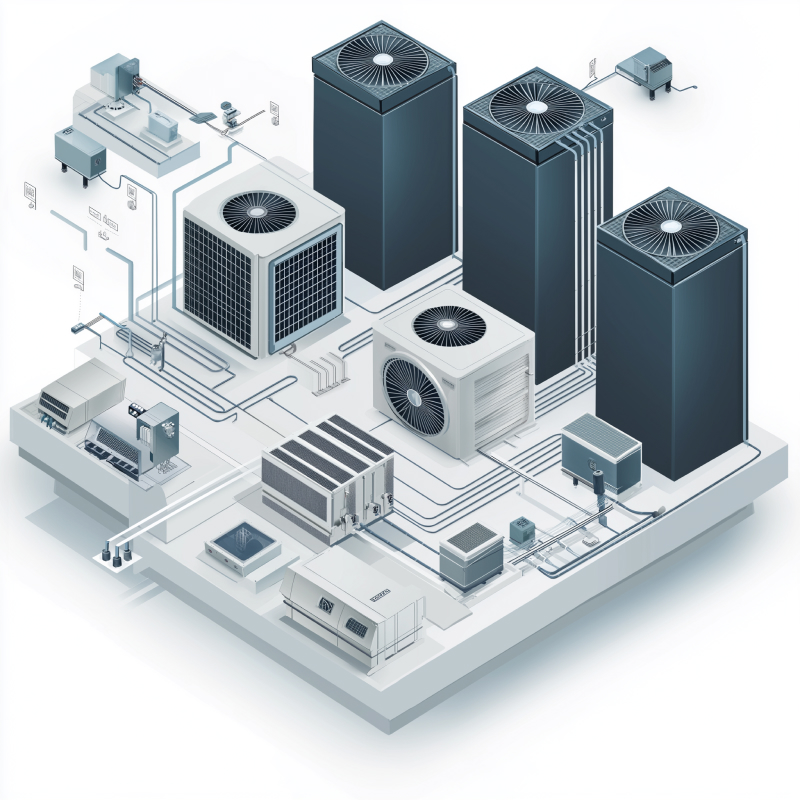
Three parallel all electric HVAC systems (air-source VRF and water-source VRF, and water-source heat pumps on a geo-exchange loop) supporting the development of energy optimization and fault detection algorithms, to keep buildings operating at their peak performance.

A diversity of space types supporting human building interaction research and can enable the development of new technologies for smart campuses and smart city solutions including energy, water, transportation, smart living and the workplace of the future.
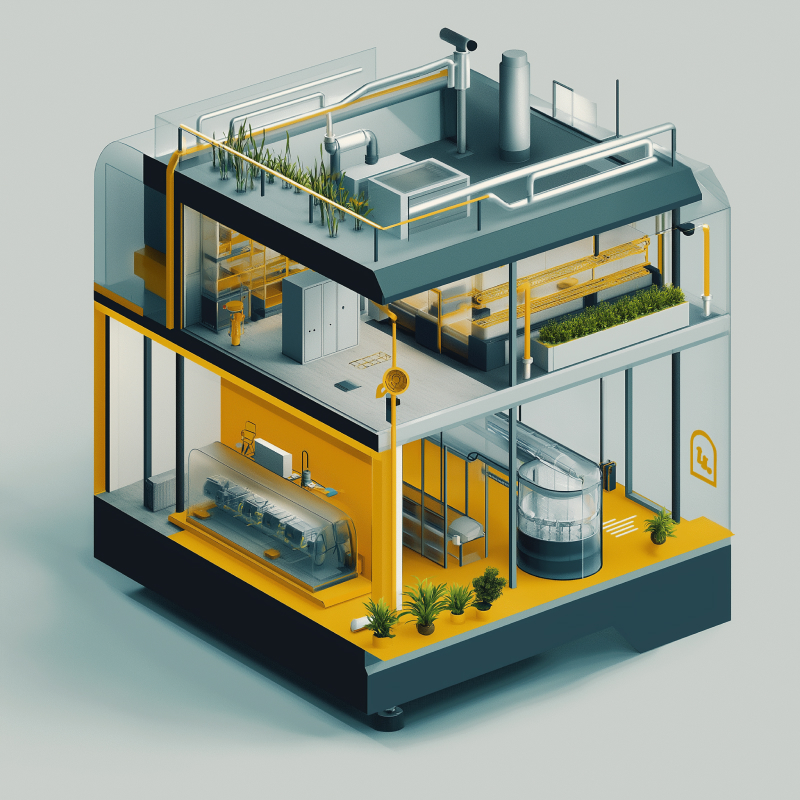

Three testbeds including a living lab where a range of building systems scenarios can be simulated in a controlled environment.

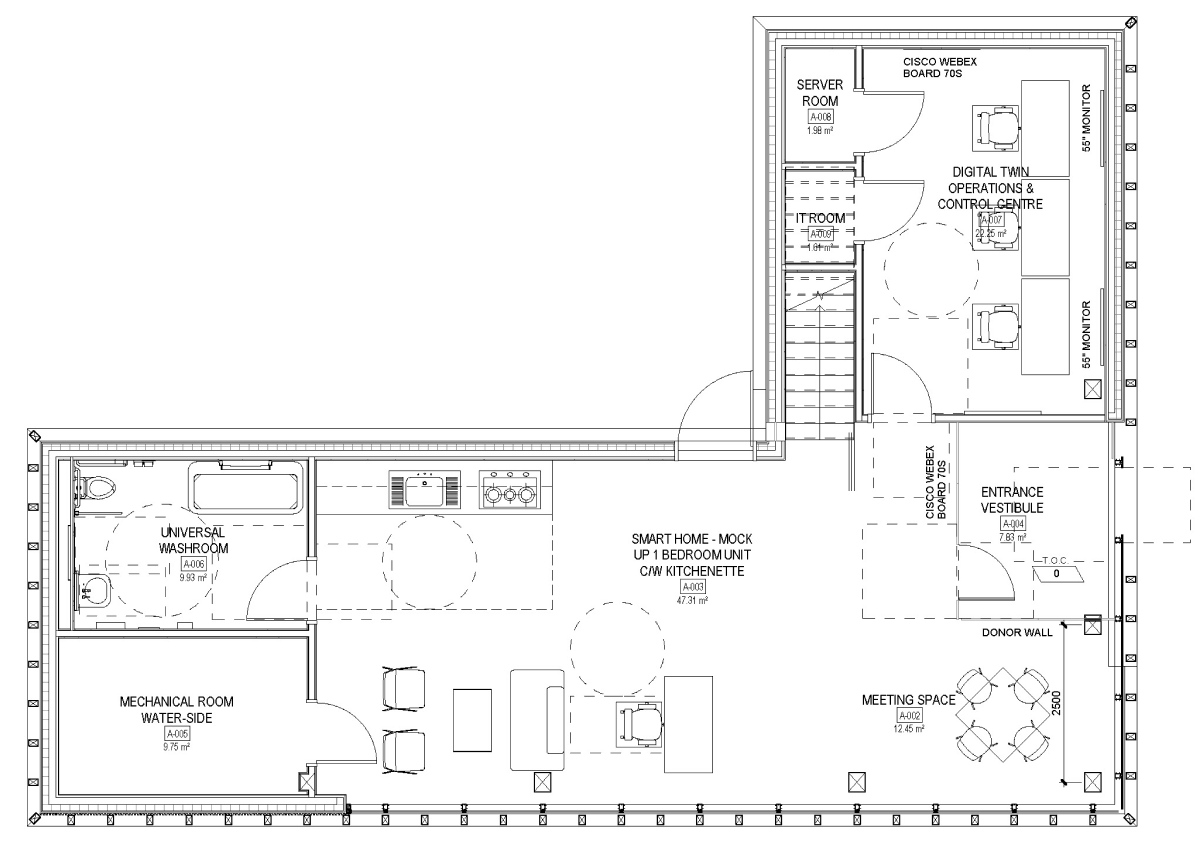
Ground Floor
The Smart Home R&D sandbox is located on the ground floor. A digital backbone ties together all of the digital equipment and sensors. These are connected to a smart command and control centre, which allows us to integrate a magnitude of building-systems information. The data from the integrated systems and from the broader campus is collected into a brain of sorts, a Cognitive Digital Twin.
The 3 HVAC systems are served by a mechanical room that ties these into a GEO exchange system allowing for high performance net-zero carbon operation.
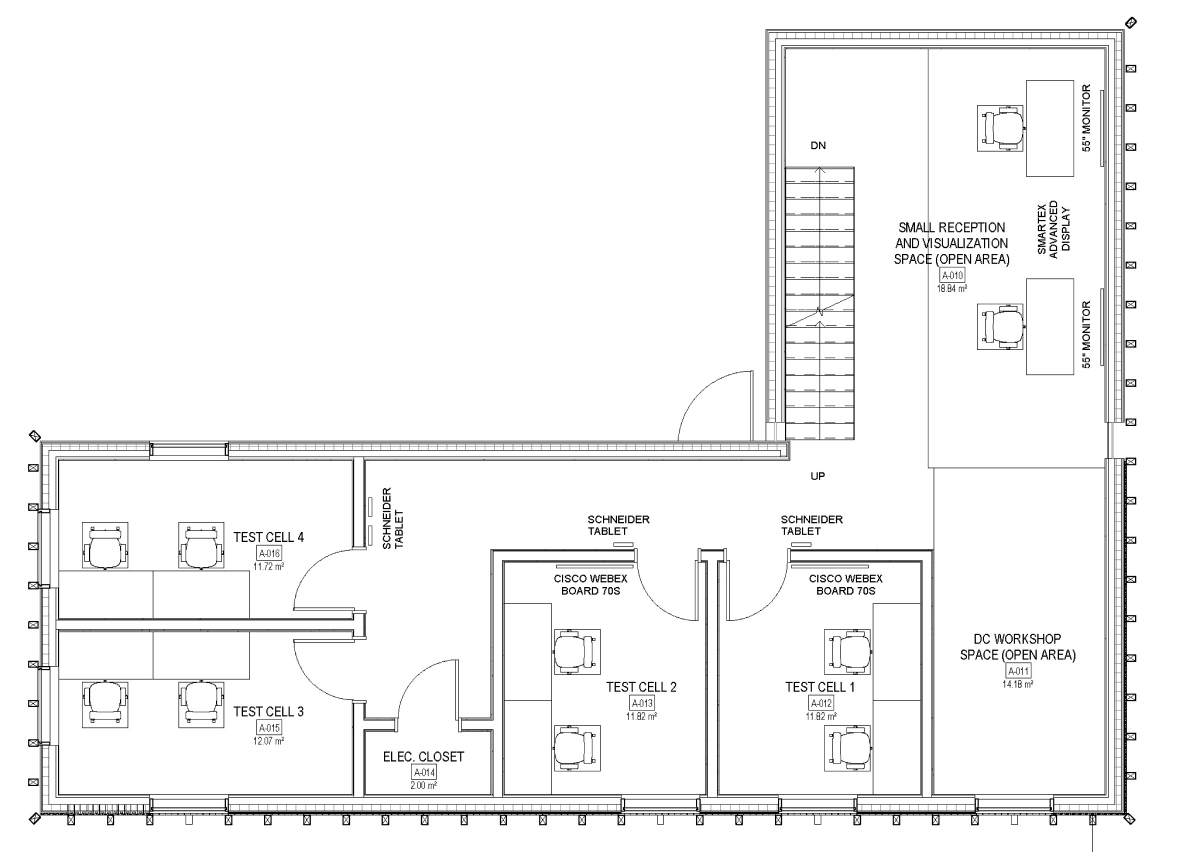
Second Floor
With an open floor plan and partition office spaces, the second floor will also be home to the Schneider Electric living lab, comprising a visualization suite, a workshop to develop test & validate Power of Ethernet (PoE) Technologies , and 4 test cells to compare these different technologies and controls in equivalent conditions.

Testbeds
SCITHub provides opportunities for researchers to collaborate and develop, test, and validate Smart Building solutions in three distinct, remotely accessible testbeds:

Smart Home (“Affordable Living Integrated Residential Testbed”)
Housed on the ground floor, this testbed provides a venue to test Smart Home solutions related to cooking, eating, sleeping, and recreation. As with the other spaces, this highly-monitored environment is equipped with two distinct HVAC systems.
This testbed acquires data from existing systems and supplements existing sensors to provide Living Lab functionality in buildings at the University of Victoria and the University of New Brunswick. This data will complement the data gathered from the TMU campus.
Smart Office (“Smart Building Analytics Living Lab”)
The Smart Building Analytics Living Lab (SBAL) is a research space that connects state-of-the-art low-carbon HVAC technologies with power management, lighting, security, and IT/communication systems. This space is equipped with essential materials to evaluate building performance throughout the operation of these integrated systems. This means researchers can acquire more accurate data and develop better strategies and applications of smart technology in residential and commercial settings.
Operations and Data Visualization Centre (ODVC)
The Operations and Data Visualization Centre (ODVC) functions like a brain where the SBAL test cells connect with a cloud-housed data ingestion, management, and analytics platform. It will process data (i.e. building automation, campus pedestrian and traffic flow sensors, campus infrastructure monitors, weather stations data, and facility management systems like maintenance, occupant complaints, space planning, etc.) from TMU’s Cognitive Digital Twin. This centre consists of 10 high-definition monitors and firewall devices to protect and stream data from the SBAL and the TMU Campus to the cloud repository.